Indication Aimovig® (erenumab-aooe) is indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.
Indication Aimovig® (erenumab-aooe) is indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.


*Injection site reactions include multiple preferred terms, such as injection site pain and injection site erythema.1
†The rate of injection site reactions reported is with the prefilled syringe.1
AE=adverse event; CM=chronic migraine; DBTP=double-blind treatment phase; EM=episodic migraine; QM=once a month.
In a phase 3 EM study
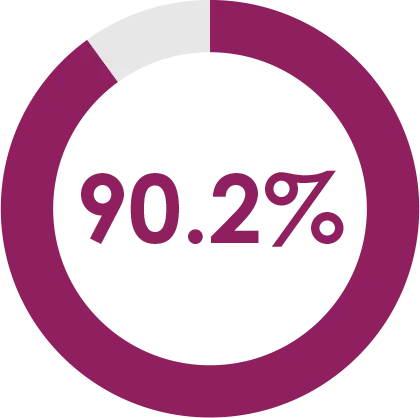
of patients with episodic migraine completed the STRIVE ATP (6 months to 1 year); 1.9% of patients discontinued due to AEs1,2,*
*The most frequently reported reasons (≥1.0% of total subjects) for discontinuation of Aimovig® were subject request (6.5%), lost to follow-up (2.0%), adverse event (1.9%), and protocol-specific criteria (1.2%).1,2
AE=adverse event; ATP=active treatment phase; CM=chronic migraine; URI=upper respiratory tract infection; UTI=urinary tract infection.
Phase 2 Episodic Migraine Open-Label Treatment Phase (OLTP) Safety Data—Through 5 Years1
Patient-years of exposure was used in this calculation to account for different lengths of treatment periods experienced by each patient.
*One fatality, previously reported, due to arteriosclerosis occurred in a patient with history of hypertension and left anterior hemiblock (ECG), who on autopsy showed evidence of severe coronary artery disease and presence of cardiac stimulants (liver tissue)—considered not related to investigational product by investigator. The other fatality was attributed to death unattended.2,3
†Events with ≥4.2 patients per 100 patient-years in the Aimovig® 70 mg/140 mg group.
‡Phase 2 EM OLTP: The most frequently reported reasons (≥1.0% of total subjects) for discontinuation of Aimovig® were subject request (21.9%), other (8.1%), adverse event (4.7%), lost to follow-up (3.4%), lack of efficacy (3.1%), and non-compliance (1.8%).1
AE=adverse event; ECG=electrocardiogram; EM=episodic migraine; n=number of patients reporting at least 1 occurrence of event; OLTP=open-label treatment phase; QM=once a month; r=exposure-adjusted rate per 100 patient-years (n/e x 100).
In a phase 2 CM study
*The most frequently reported reasons (≥1.0% of total subjects) for discontinuation of Aimovig® were subject request (10.5%), lack of efficacy (6.4%), adverse event (2.6%), and lost to follow-up (1.5%).2
AE=adverse event; CM=chronic migraine; OLE=open-label extension; URI=upper respiratory tract infection; UTI=urinary tract infection.
In a phase 4 CM with MOH study


†The most frequently reported reasons (≥1.0% of total subjects) for discontinuation were noncompliance (1.4%), adverse event (1.5%), and subject request (2.6%).
CM=chronic migraine; DBTP=double-blind treatment phase; Q4W=once every 4 weeks; TEAEs=treatment emergent adverse events.
Contraindication: Aimovig® is contraindicated in patients with serious hypersensitivity to erenumab-aooe or to any of the excipients. Reactions have included anaphylaxis and angioedema.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions, including rash, angioedema, and anaphylaxis, have been reported with Aimovig® in post marketing experience. Most reactions were not serious and occurred within hours of administration, although some occurred more than one week after administration. If a serious or severe reaction occurs, discontinue Aimovig® and initiate appropriate therapy.
Constipation with Serious Complications: Constipation with serious complications has been reported following the use of Aimovig® in the postmarketing setting. There were cases that required hospitalization, including cases where surgery was necessary. The onset of constipation was reported after the first dose in a majority of these cases, but patients also reported later on in treatment. Aimovig® was discontinued in most reported cases. Constipation was one of the most common (up to 3%) adverse reactions reported in clinical studies.
Monitor patients treated with Aimovig® for severe constipation and manage as clinically appropriate. Concurrent use of medications associated with decreased gastrointestinal motility may increase the risk for more severe constipation and the potential for constipation-related complications.
Hypertension: Development of hypertension and worsening of pre-existing hypertension have been reported following the use of Aimovig® in the postmarketing setting. Many of the patients had pre-existing hypertension or risk factors for hypertension. There were cases requiring pharmacological treatment and, in some cases, hospitalization. Hypertension may occur at any time during treatment but was most frequently reported within seven days of dose administration. In the majority of the cases, the onset or worsening of hypertension was reported after the first dose. Aimovig® was discontinued in many of the reported cases.
Monitor patients treated with Aimovig® for new-onset hypertension, or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, and consider whether discontinuation of Aimovig® is warranted if evaluation fails to establish an alternative etiology.
Raynaud's Phenomenon: Development of Raynaud’s phenomenon and recurrence or worsening of preexisting Raynaud’s phenomenon have been reported in the postmarketing setting following the use of CGRP antagonists, including AIMOVIG. Many of the cases reported serious outcomes, including hospitalizations and disability, generally related to debilitating pain.
AIMOVIG should be discontinued if signs or symptoms of Raynaud’s phenomenon develop, and patients should be evaluated by a healthcare provider if symptoms do not resolve. Patients with a history of Raynaud’s phenomenon should be monitored for, and informed about the possibility of, worsening or recurrence of signs and symptoms.
Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions in clinical studies (≥ 3% of Aimovig®-treated patients and more often than placebo) were injection site reactions and constipation.
Aimovig® (erenumab-aooe) is indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.
Please see Aimovig® full Prescribing Information.
Contraindication: Aimovig® is contraindicated in patients with serious hypersensitivity to erenumab-aooe or to any of the excipients. Reactions have included anaphylaxis and angioedema.
Hypersensitivity reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions, including rash, angioedema, and anaphylaxis, have been reported with Aimovig® in post marketing experience. Most reactions were not serious and occurred within hours of administration, although some occurred more than one week after administration. If a serious or severe
Reference: 1. Aimovig. Package insert. Amgen Inc; 2025.
References: 1. Goadsby PJ, Reuter U, Hallström Y, et al. One-year sustained efficacy of erenumab for episodic migraine: Results of the STRIVE study. Neurology. 2020;95:e469-e479. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000010019. 2. Data on file, Amgen; [Ph 3 EM CSR, July 16, 2018].
References: 1. Ashina M, Goadsby PJ, Reuter U, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of erenumab in migraine prevention: Results from a 5-year, open-label treatment phase of a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Neurol. 2021;28:1716-1725. doi:10.1111/ene.14175. 2. Ashina M, Goadsby PJ, Reuter U, et al. Long-term safety and tolerability of erenumab: three-plus year results from an ongoing open-label extension study in episodic migraine. Presented at: American Headache Society 60th Annual Meeting; June 28-July 1, 2018; San Francisco, CA. 3. Data on file, Amgen; [Ph 2 EM CSR Table 14-6.1.405, September 2, 2021]. 4. Data on file, Amgen; [Ph 2 EM CSR, Table 9-3, June 16, 2020].
References: 1. Tepper SJ, Ashina M, Reuter U, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of erenumab in patients with chronic migraine: Results from a 52-week, open-label extension study. Cephalalgia. 2020;40(6):543-553. 2. Data on file, Amgen; [Ph 2 CM CSR, February 16, 2018]. 3. Tepper SJ, Dodick D, Lanteri-Minet M, et al. A Phase 4 Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Erenumab in Adults with Medication Overuse Headache. Poster presented at: American Headache Society 65th Annual Scientific Meeting; June 15-18, 2023; Austin, TX.